Blocking and Non-Blocking Algorithms
/
0 Comments
Blocking, non-blocking, lock-free, and wait-free. Each of these terms describes a key characteristic…
Malicious Race Conditions and Data Races
This post is about malicious race conditions and data races. Malicious race conditions are race conditions…
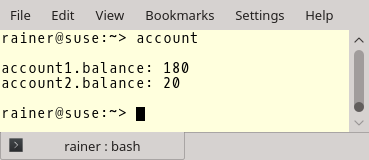
Race Conditions versus Data Races
Race conditions and data races are related but different concepts. Because they are related, they are…
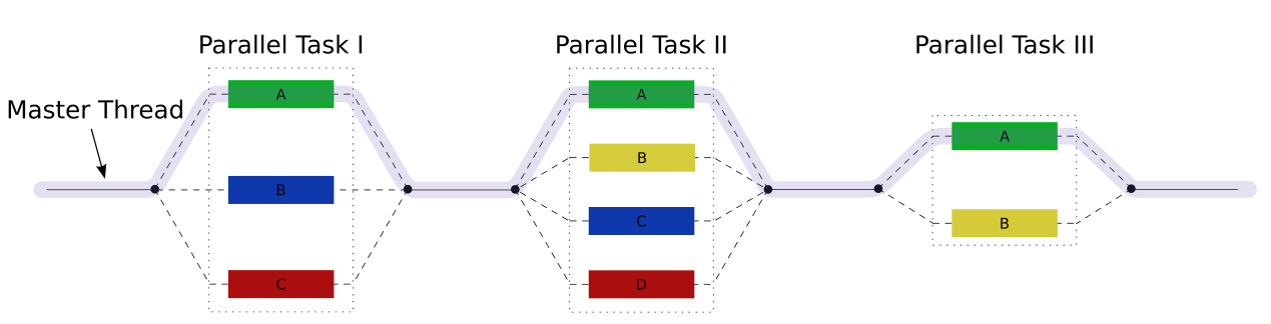
Task Blocks
Task blocks use the well-known fork-join paradigm for the parallel execution of tasks.
Who invented…
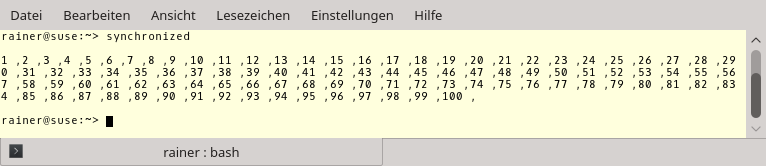
Transactional Memory
Transactional memory is based on the idea of a transaction from the database theory. Transactional memory…
Coroutines
Coroutines are functions that can suspend and resume their execution while keeping their state. The evolution…
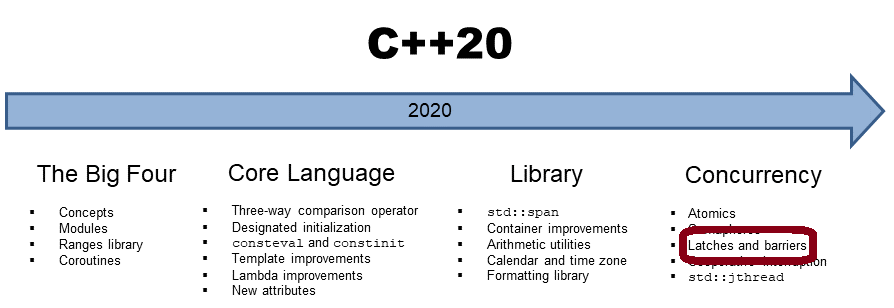
Latches And Barriers
Latches and barriers are simple thread synchronization mechanisms, enabling some threads to wait until…

std::future Extensions
Tasks in the form of promises and futures have in C++11 an ambivalent reputation. On the one hand, they…

Atomic Smart Pointers
C++20 will have atomic smart pointers. To be exact, we will get a std::atomic_shared_ptr and a std::atomic_weak_ptr.…

Parallel Algorithms of the Standard Template Library
The idea is quite simple. The Standard Template has more than 100 algorithms for searching, counting,…
