C++ Core Guidelines: Rules for Allocating and Deallocating
The guidelines have six rules for explicit memory allocation and deallocation. Six! Maybe you are surprised because there is a simple rule in modern C++: don’t use new and delete. The story is not so simple.

Here are the six rules.
- R.10: Avoid
malloc()andfree() - R.11: Avoid calling
newanddeleteexplicitly - R.12: Immediately give the result of an explicit resource allocation to a manager object
- R.13: Perform at most one explicit resource allocation in a single expression statement
- R.14: ??? array vs. pointer parameter
- R.15: Always overload matched allocation/deallocation pairs
I will not write about the last two rules. First, rule R.14 is not baked enough, and second, rule R.15 is quite special. If you want to learn more about overloading new and delete, you should read my posts on memory allocation and deallocation.
Before I dive into the rules, let me give you a little background necessary for understanding the rules. Creating an object in C++ with new consists of two steps.
- Allocate the memory for the object
- Constructing the object into the allocated memory
operator new or operator new [] makes the first step; the constructor the second step.
The same strategy applies to the destruction but the other way around. First, the destructor is called (if any), and then the memory is deallocated with operator delete or operator delete []. This two-step creation and destruction is the reason for the four rules. So, let’s start.
R.10: Avoid malloc() and free()
What is the difference between new and malloc, or delete and free? The C-functions malloc and free do only half of the job. malloc allocates the memory and free only deallocates the memory. Neither does malloc invoke the constructor, nor does free invoke the destructor.
This means if you use an object which was just created via malloc, you will get undefined behavior.
// mallocVersusNew.cpp #include <iostream> #include <string> struct Record{ Record(std::string na = "Record"): name(na){} // (4) std::string name; }; int main(){ std::cout << std::endl; Record* p1 = static_cast<Record*>(malloc(sizeof(Record))); // (1) std::cout << p1->name << std::endl; // (3) auto p2 = new Record; // (2) std::cout << p2->name << std::endl; std::cout << std::endl; }
I only allocate in (1) memory for my Record object. The result is that the output p1->name in (3) is undefined behavior. In contrast, call (2) invokes the constructor in line (4). Undefined behavior means that you can not make any assumptions about the program’s output.
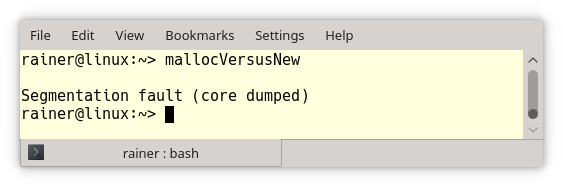
Depending on the used platform and the used GCC, the result of the program is entirely different.
- GCC 4.8.5 produces a core dump on my local PC
 Modernes C++ Mentoring
Modernes C++ Mentoring
Do you want to stay informed: Subscribe.
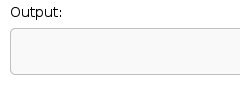
- GCC 4.9 (on cppreference.com) produces no output
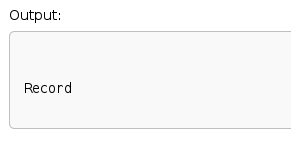
- GCC 7.1 (cppreference.com) produces the expected output
R.11: Avoid calling new and delete explicitly
You should keep this rule in mind. The emphasis in this rule lies on the word explicitly because using smart pointers or containers of the Standard Template Library gives you the object which use implicitly new and delete.
R.12: Immediately give the result of an explicit resource allocation to a manager object
This is the key idea of a smart pointer such as std::unique_ptr<int> upInt(new int()) and will not hold in the counterexample from the guidelines. If the allocation of the buffer fails, the file handle will be lost.
void f(const std::string& name) { FILE* f = fopen(name, "r"); // open the file std::vector<char> buf(1024); fclose(f); // close the file }
R.13: Perform at most one explicit resource allocation in a single expression statement
This rule is a little bit tricky.
void func(std::shared_ptr<Widget> sp1, std::shared_ptr<Widget> sp2){ ... } func(std::shared_ptr<Widget>(new Widget(1)), std::shared_ptr<Widget>(new Widget(2)));
This function call is not exception-safe and may result in a memory leak. Why? The reason is that four operations must be performed to initialize the shared pointers.
- Allocate memory for Widget(1)
- Construct Widget(1)
- Allocate memory for Widget(2)
- Construct Widget(2)
The compiler can allocate the memory for Widget(1) and Widget(2) and then construct both.
- Allocate memory for Widget(1)
- Allocate memory for Widget(2)
- Construct Widget(1)
- Construct Widget(2)
If one of the constructors throws an exception, the memory of the other object will not be automatically freed, and we will get a memory leak.
It’s easy to overcome this issue using the factory function std::make_shared to create a std::shared_ptr.
func(std::make_shared<Widget>(1), std::make_shared<Widget>(2));
std::make_shared guarantees that the function will have no effect if an exception is thrown. The pendant function std::make_unique for creating a std::unique_ptr guarantees the same.
What’s next?
The next rules to resource management will follow Rule R.11: avoid calling new and delete explicitly; therefore, the next post will be about the smart pointers std::unique_ptr, std::shared_ptr, and std::weak_ptr.
Thanks a lot to my Patreon Supporters: Matt Braun, Roman Postanciuc, Tobias Zindl, G Prvulovic, Reinhold Dröge, Abernitzke, Frank Grimm, Sakib, Broeserl, António Pina, Sergey Agafyin, Андрей Бурмистров, Jake, GS, Lawton Shoemake, Jozo Leko, John Breland, Venkat Nandam, Jose Francisco, Douglas Tinkham, Kuchlong Kuchlong, Robert Blanch, Truels Wissneth, Mario Luoni, Friedrich Huber, lennonli, Pramod Tikare Muralidhara, Peter Ware, Daniel Hufschläger, Alessandro Pezzato, Bob Perry, Satish Vangipuram, Andi Ireland, Richard Ohnemus, Michael Dunsky, Leo Goodstadt, John Wiederhirn, Yacob Cohen-Arazi, Florian Tischler, Robin Furness, Michael Young, Holger Detering, Bernd Mühlhaus, Stephen Kelley, Kyle Dean, Tusar Palauri, Juan Dent, George Liao, Daniel Ceperley, Jon T Hess, Stephen Totten, Wolfgang Fütterer, Matthias Grün, Phillip Diekmann, Ben Atakora, Ann Shatoff, Rob North, Bhavith C Achar, Marco Parri Empoli, Philipp Lenk, Charles-Jianye Chen, Keith Jeffery, Matt Godbolt, Honey Sukesan, bruce_lee_wayne, Silviu Ardelean, schnapper79, Seeker, and Sundareswaran Senthilvel.
Thanks, in particular, to Jon Hess, Lakshman, Christian Wittenhorst, Sherhy Pyton, Dendi Suhubdy, Sudhakar Belagurusamy, Richard Sargeant, Rusty Fleming, John Nebel, Mipko, Alicja Kaminska, Slavko Radman, and David Poole.
| My special thanks to Embarcadero |  |
| My special thanks to PVS-Studio |  |
| My special thanks to Tipi.build |  |
| My special thanks to Take Up Code |  |
| My special thanks to SHAVEDYAKS |  |
Modernes C++ GmbH
Modernes C++ Mentoring (English)
Rainer Grimm
Yalovastraße 20
72108 Rottenburg
Mail: schulung@ModernesCpp.de
Mentoring: www.ModernesCpp.org





Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!