Chrono: Input
You can also apply the format specifier for formatted input.
This post is the eleventh in my detailed journey through the chrono extension in C++20.
- Basic Chrono Terminology
- Basic Chrono Terminology with Time Duration and Time Point
- Time of Day: Details
- Creating Calendar Dates
- Displaying and Checking Calendar Dates
- Query Calendar Dates and Ordinal Dates
- Time Zones: Details
- Time Zones: Online Classes
- Chrono: I/O
- Chrono: I/O: Unformatted
The chrono library supports formatted input in two ways. You can use the function std::chrono::from_stream or std::chrono::parse. Both functions require an input stream and parse the input into a time point according to the format specification. All format specifier except %q for unit suffixed according to the literals for time durations can be used.
std::chrono::from_stream
std::chrono::from_stream has overloads for the various clocks.
Clocks
std::chrono::system_timestd::chrono::utc_timestd::chrono::tai_timestd::chrono::gps_timestd::chrono::file_timestd::chrono::local_time
Calendar dates
std::chrono::year_month_daystd::chrono::year_monthstd::chrono::month_daystd::chrono::weekdaystd::chrono::yearstd::chrono::monthstd::chrono::day
The various overloads require in the elementary form an input stream is, a format string fmt, and a time point or a calendar object chro: std::chrono::from_stream(is, fmt, chro). The chrono object from the input stream is then parsed according to the format string.
You can also provide an abbreviation abb for a time zone and an offset off to the UTC time: std::chrono::from_stream(is, fmt, chro, abb, off). The offset has the type std::chrono::minutes.
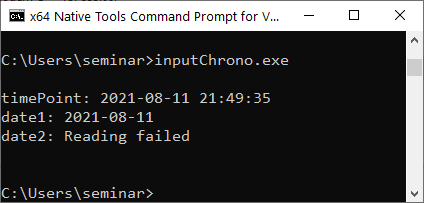
The program inputChrono.cpp uses formatted input to read a time point and a calendar date from an input stream.
// inputChrono.cpp #include <chrono> #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <sstream> int main() { std::cout << '\n'; std::chrono::sys_seconds timePoint; std::istringstream iStream1{"2021-08-11 21:49:35"}; //(1) std::chrono::from_stream(iStream1, "%F %T", timePoint); //(2) if (iStream1) std::cout << "timePoint: " << timePoint << '\n'; else std::cerr << "timepoint: Reading failed\n"; std::chrono::year_month_day date1; std::istringstream iStream2{"11/08/21"}; //(3) std::chrono::from_stream(iStream2, "%x", date1); //(4) if (iStream2) std::cout << "date1: " << date1 << '\n'; else std::cerr << "date1: Reading failed\n"; std::chrono::year_month_day date2; std::istringstream iStream3{"11/15/21"}; std::chrono::from_stream(iStream3, "%x", date2); //(5) if (iStream3) std::cout << "date2: " << date2 << '\n'; else std::cerr << "date2: Reading failed\n"; std::cout << '\n'; }
On lines 1 and 2, the data on the input stream (iStream1) matches the format string (“%F %T"). The same holds for input stream iStream2 (line 3) and the corresponding format string “%x" (line 4). On the contrary, there is no 15th month, and the parse step in line 5 fails. Consequentially, the failbit of the iStream3 is set. Using the iStream3 in a boolean expression evaluates to false.
std::chrono::parse
Accordingly to std::chrono::from_stream, you can use the function std::chrono::parse for parsing input. The following code snippet shows their equivalence.
std::chrono::from_stream(is, fmt, chro) is >> std::chrono::parse(fmt, chro)
Instead of std::chrono::from_stream, std::chrono::parse is directly invoked on the input stream is. std::chrono::parse also needs a format string fmt and a chrono object chro.
Consequently, I can directly rewrite the previous program inputChrono.cpp using std::chrono::from_stream into the program inputChronoParse.cpp using std::chrono::parse.
// inputChronoParse.cpp #include <chrono> #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <sstream> int main() { std::cout << '\n'; std::chrono::sys_seconds timePoint; std::istringstream iStream1{"2021-08-11 21:49:35"}; iStream1 >> std::chrono::parse("%F %T", timePoint); if (iStream1) std::cout << "timePoint: " << timePoint << '\n'; else std::cerr << "timepoint: Reading failed\n"; std::chrono::year_month_day date1; std::istringstream iStream2{"11/08/21"}; iStream2 >> std::chrono::parse("%x", date1); if (iStream2) std::cout << "date1: " << date1 << '\n'; else std::cerr << "date1: Reading failed\n"; std::chrono::year_month_day date2; std::istringstream iStream3{"11/15/21"}; iStream3 >> std::chrono::parse("%x", date2); if (iStream3) std::cout << "date2: " << date2 << '\n'; else std::cerr << "date2: Reading failed\n"; std::cout << '\n'; }
What’s Next?
I’m done with my deep dive into the chrono library. In my next post, I will discuss concurrency.
Thanks a lot to my Patreon Supporters: Matt Braun, Roman Postanciuc, Tobias Zindl, G Prvulovic, Reinhold Dröge, Abernitzke, Frank Grimm, Sakib, Broeserl, António Pina, Sergey Agafyin, Андрей Бурмистров, Jake, GS, Lawton Shoemake, Jozo Leko, John Breland, Venkat Nandam, Jose Francisco, Douglas Tinkham, Kuchlong Kuchlong, Robert Blanch, Truels Wissneth, Mario Luoni, Friedrich Huber, lennonli, Pramod Tikare Muralidhara, Peter Ware, Daniel Hufschläger, Alessandro Pezzato, Bob Perry, Satish Vangipuram, Andi Ireland, Richard Ohnemus, Michael Dunsky, Leo Goodstadt, John Wiederhirn, Yacob Cohen-Arazi, Florian Tischler, Robin Furness, Michael Young, Holger Detering, Bernd Mühlhaus, Stephen Kelley, Kyle Dean, Tusar Palauri, Juan Dent, George Liao, Daniel Ceperley, Jon T Hess, Stephen Totten, Wolfgang Fütterer, Matthias Grün, Phillip Diekmann, Ben Atakora, Ann Shatoff, Rob North, Bhavith C Achar, Marco Parri Empoli, Philipp Lenk, Charles-Jianye Chen, Keith Jeffery, Matt Godbolt, Honey Sukesan, bruce_lee_wayne, Silviu Ardelean, schnapper79, Seeker, and Sundareswaran Senthilvel.
 Modernes C++ Mentoring
Modernes C++ Mentoring
Do you want to stay informed: Subscribe.
Thanks, in particular, to Jon Hess, Lakshman, Christian Wittenhorst, Sherhy Pyton, Dendi Suhubdy, Sudhakar Belagurusamy, Richard Sargeant, Rusty Fleming, John Nebel, Mipko, Alicja Kaminska, Slavko Radman, and David Poole.
| My special thanks to Embarcadero |  |
| My special thanks to PVS-Studio |  |
| My special thanks to Tipi.build |  |
| My special thanks to Take Up Code |  |
| My special thanks to SHAVEDYAKS |  |
Modernes C++ GmbH
Modernes C++ Mentoring (English)
Rainer Grimm
Yalovastraße 20
72108 Rottenburg
Mail: schulung@ModernesCpp.de
Mentoring: www.ModernesCpp.org