Posts

A Lock-Free Stack: Atomic Smart Pointer
The easiest way to solve this memory leak issue from the last post is to use a std::shared_ptr.
Atomic…
Covariant Return Type
/
0 Comments
The Covariant Return Type of a member function allows an overriding member function to return a narrower…
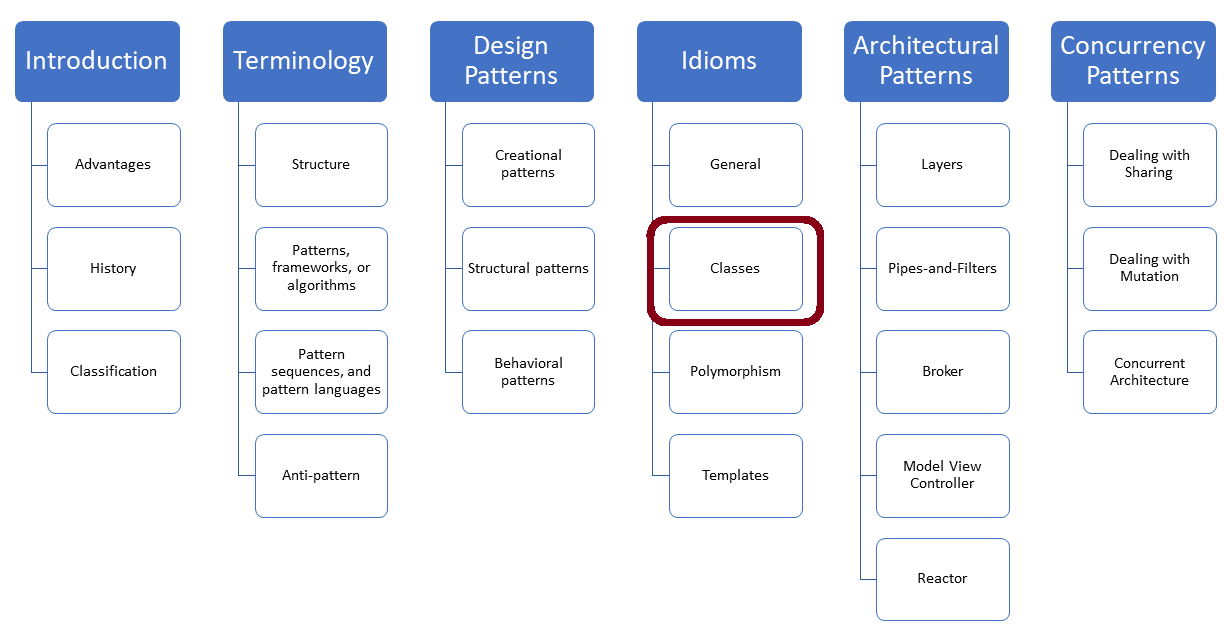
The Proxy Pattern
The Proxy Pattern is probably the most influential design pattern for C++. The Proxy provides a placeholder…

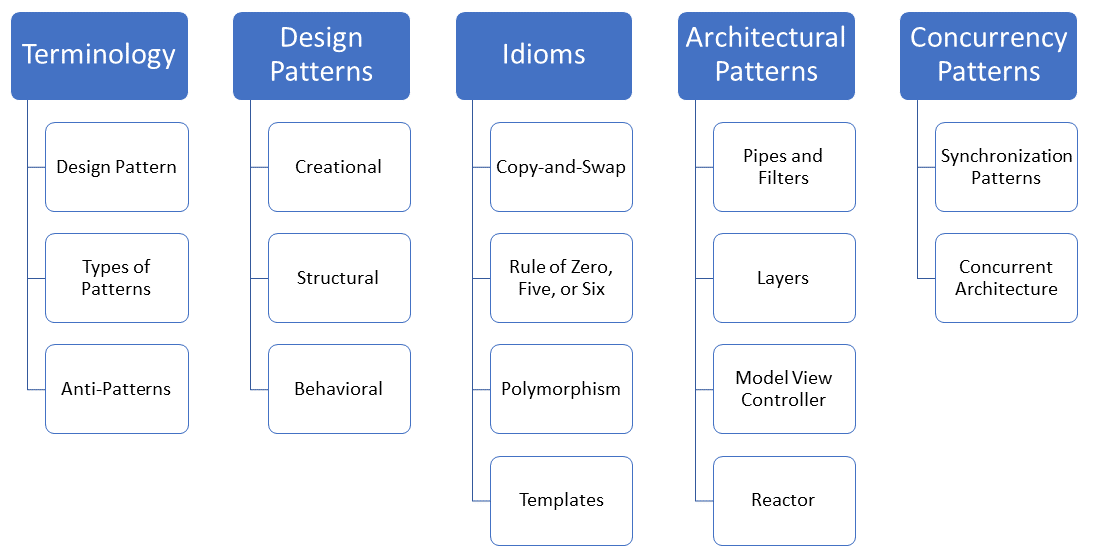
The Bridge Pattern
The Bridge Pattern is a structural pattern. It decouples the interface from the implementation. In C++,…
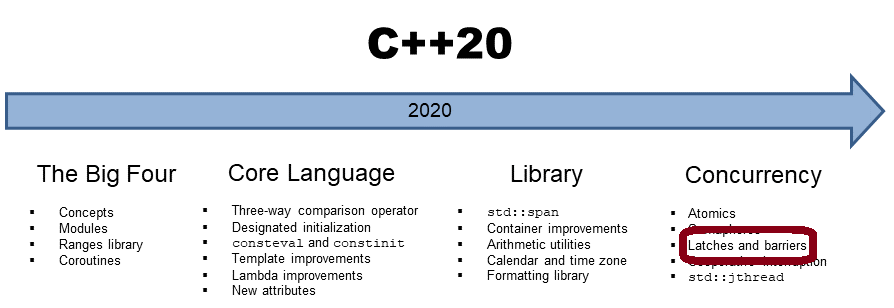
Barriers and Atomic Smart Pointers in C++20
In my last post, I introduced latches in C++20. A latch enables its threads to wait until a counter becomes…

C++ Core Guidelines: Passing Smart Pointers
Passing smart pointers is a critical topic that is seldom addressed. This ends with the C++ core guidelines…

C++ Core Guidelines: Rules for Smart Pointers
There were a lot of C++ experts who said that smart pointers were the essential feature of C++11. Today,…
Atomic Smart Pointers
C++20 will have atomic smart pointers. To be exact, we will get a std::atomic_shared_ptr and a std::atomic_weak_ptr.…
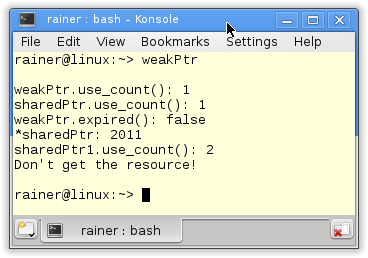
std::weak_ptr
std::unique_ptr models the concept of exclusive ownership, std::shared_ptr the concept of shared ownership.…

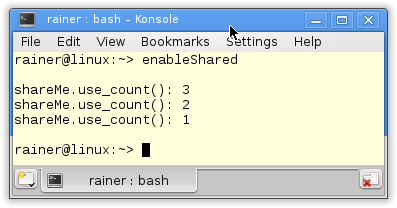
Specialities of std::shared_ptr
After I draw the big picture of a std::shared_ptr in the last post, I want to present two special aspects…
