Ongoing Optimization: Sequential Consistency with CppMem
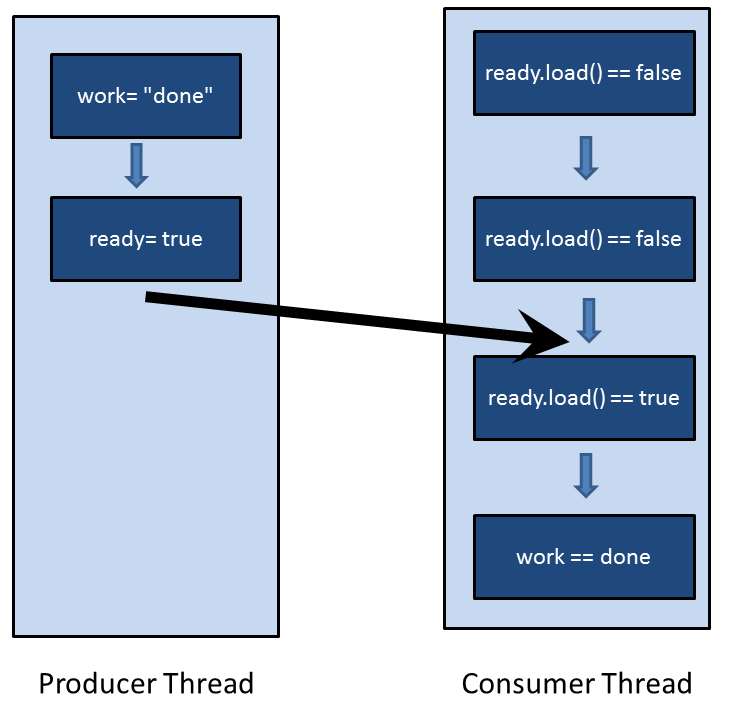
With atomic data types, you can tailor your program to your needs and optimize it. But now we are in the domain of multithreading experts.
Sequential consistency
If you don’t specify the memory model, sequential consistency will be used. The sequential consistency guarantees two properties. Each thread executes its instructions in source code order, and all threads follow a global order.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
// OngoingOptimizationSequentialConsistency.cpp #include <atomic> #include <iostream> #include <thread> std::atomic<int> x{0}; std::atomic<int> y{0}; void writing(){ x.store(2000); y.store(11); } void reading(){ std::cout << y.load() << " "; std::cout << x.load() << std::endl; } |
This knowledge is sufficient to analyze the program. Because x and y are atomic, the program has no race condition. So there is only the question. What values are possible for x and y? But the question is easy to answer. Because of the sequential consistency, all threads must follow a global order.
It holds:
- x.store(2000); happens-before y.store(11);
- std::cout << y.load() << ” “; happens-before std::cout << x.load() << std::endl;
Therefor: x.load() can not have 0, if y.load() is 11, because x.store(2000) happens before y.store(11).
All other values for x and y are possible. Here are three possible interleavings, producing the three different results for x and y.
- thread1 will be completely executed before thread2.
- thread2 will be completely executed before thread1.
- thread1 executes the first instruction x.store(2000), before thread2 will be completely executed.
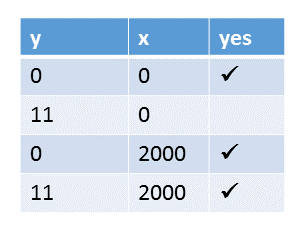
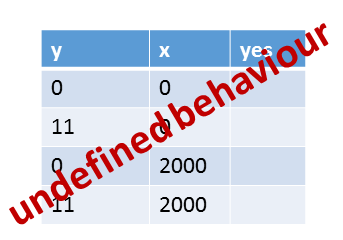
Here all values for x and y.
 Modernes C++ Mentoring
Modernes C++ Mentoring
Do you want to stay informed: Subscribe.
So how does this look like in CppMem.
CppMem
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
int main(){
atomic_int x= 0;
atomic_int y= 0;
{{{ {
x.store(2000);
y.store(11);
}
||| {
y.load();
x.load();
}
}}}
}
|
At first a little bit of syntax of CppMem. CppMem uses in line 2 and 3 the typedef atomic_int for std::atomic<int>.
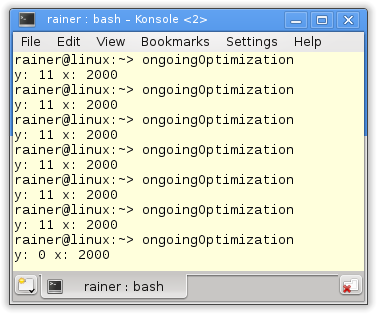
If I execute the program, I’m overwhelmed by the sheer number of execution candidates.
384 (1) possible execution candidates, and only 6 of them are consistent. No candidate has a data race. How does that work?
But I’m only interested in consistent executions. I use interface (2) to analyze the six annotated graphs. The other (378) are not consistent. That means, for example, they do not respect the modification order. So I totally ignore them.
We know already that all values for x and y are possible, except for y= 11 and x= 0. That’s because of the default memory model.

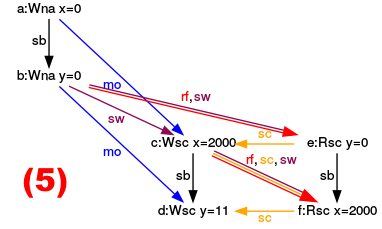
Now the questions are. Which interleavings of the threads produce which values for x and y? I already introduce the symbols in the annotated graph (CppMem – An overview); therefore, I will concentrate my analysis on the results for x and y.
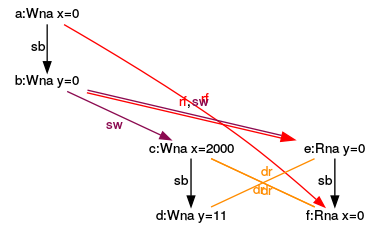
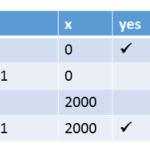
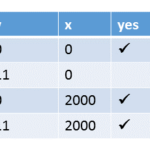
Execution for (y= 0, x= 0)
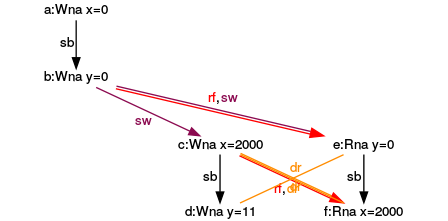
Executions for (y= 0, x= 2000)
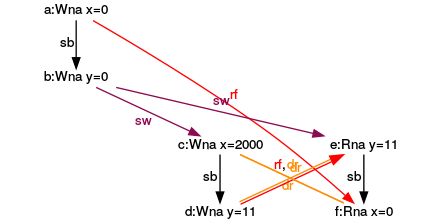
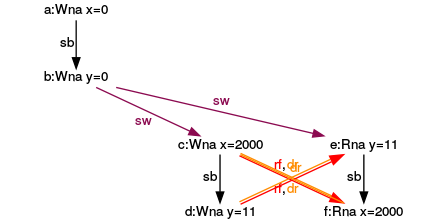
Execution for (y= 11, x= 2000)
Do you know why I used the red numbers in the graphs? I have because I’m not done with my analysis.
Deeper insights
If I look at the six different thread interleavings in the following graphic, I have the question? Which sequence of instructions corresponds to which graph? Here is the solution. I have assigned to each sequence of instructions the corresponding graph.
Sequences of instructions
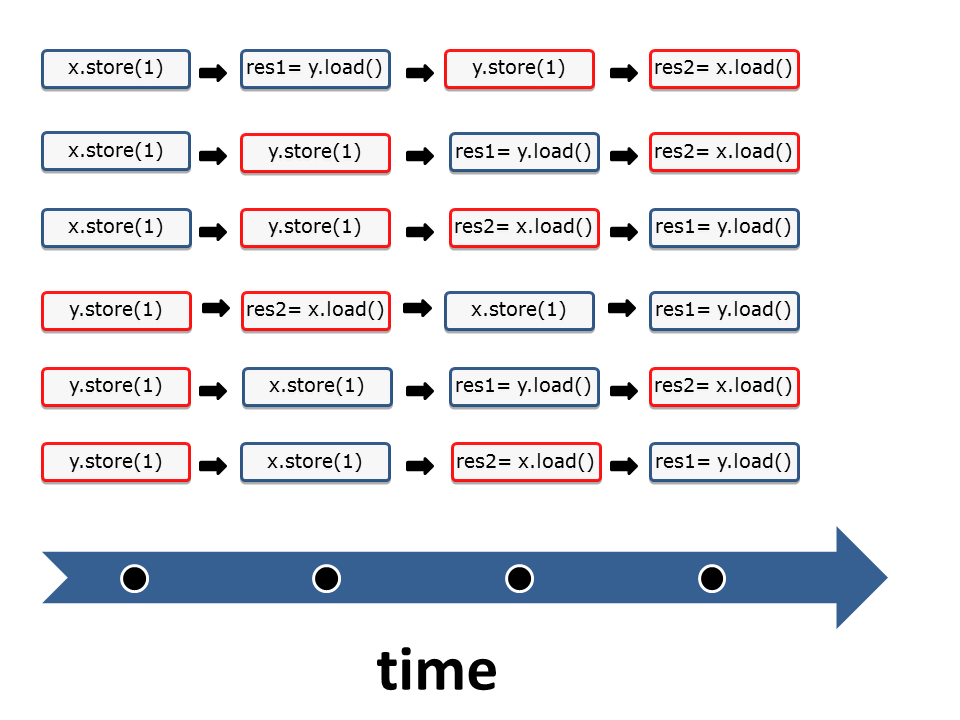
I start with the simpler cases:
- (1): It’s quite simple to assign the graph (1) to the sequence (1). In the sequence (1) have x and y the values 0, because y.load() and x.load() are executed before the operations x.store(2000) and y.store(11).
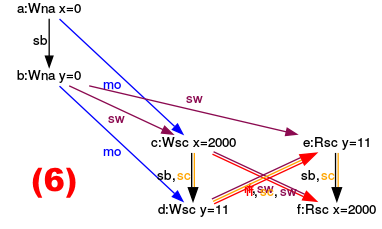
- (6): The argumentation for the execution (6) is accordingly. y has the value 11 and y the value 2000 if all load operations happen after all store operations.
- (2),(3),(4),(5): Now to the more interesting cases, in which y has den value 0 and x has the value 2000. The yellow arrows (sc) are the key to my reasoning because they stand for the sequence of instructions. For example, let’s look at execution (2).
- (2): The sequence of the yellow arrows (sc) in the graph (2) is: Write x= 2000 => Read y= 0 => Write y= 11 => Read x= 2000. This corresponds to the instructions of the second interleaving of threads (2).
What’s next?
In the next post, I will break the sequential consistency. So what will happen if a base my optimization on the acquire-release semantic?
Thanks a lot to my Patreon Supporters: Matt Braun, Roman Postanciuc, Tobias Zindl, G Prvulovic, Reinhold Dröge, Abernitzke, Frank Grimm, Sakib, Broeserl, António Pina, Sergey Agafyin, Андрей Бурмистров, Jake, GS, Lawton Shoemake, Jozo Leko, John Breland, Venkat Nandam, Jose Francisco, Douglas Tinkham, Kuchlong Kuchlong, Robert Blanch, Truels Wissneth, Mario Luoni, Friedrich Huber, lennonli, Pramod Tikare Muralidhara, Peter Ware, Daniel Hufschläger, Alessandro Pezzato, Bob Perry, Satish Vangipuram, Andi Ireland, Richard Ohnemus, Michael Dunsky, Leo Goodstadt, John Wiederhirn, Yacob Cohen-Arazi, Florian Tischler, Robin Furness, Michael Young, Holger Detering, Bernd Mühlhaus, Stephen Kelley, Kyle Dean, Tusar Palauri, Juan Dent, George Liao, Daniel Ceperley, Jon T Hess, Stephen Totten, Wolfgang Fütterer, Matthias Grün, Ben Atakora, Ann Shatoff, Rob North, Bhavith C Achar, Marco Parri Empoli, Philipp Lenk, Charles-Jianye Chen, Keith Jeffery, Matt Godbolt, Honey Sukesan, bruce_lee_wayne, Silviu Ardelean, schnapper79, Seeker, and Sundareswaran Senthilvel.
Thanks, in particular, to Jon Hess, Lakshman, Christian Wittenhorst, Sherhy Pyton, Dendi Suhubdy, Sudhakar Belagurusamy, Richard Sargeant, Rusty Fleming, John Nebel, Mipko, Alicja Kaminska, Slavko Radman, and David Poole.
| My special thanks to Embarcadero |  |
| My special thanks to PVS-Studio |  |
| My special thanks to Tipi.build |  |
| My special thanks to Take Up Code |  |
| My special thanks to SHAVEDYAKS |  |
Modernes C++ GmbH
Modernes C++ Mentoring (English)
Rainer Grimm
Yalovastraße 20
72108 Rottenburg
Mail: schulung@ModernesCpp.de
Mentoring: www.ModernesCpp.org



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!