C++26 Core Language: Small Improvements
There are more small improvements in the C++26 language, which you should know.

static_assert extension
First, here’s the syntax of static_assert in C++11:
static_assert(compile time predicate, unevaluated string)
With C++26, the string can be a user-defined type having the following properties:
- Has a
size()method that produces an integer - Has a
data()method that produces a pointer of character type such that - The elements in the
range [data(), data()+size())are valid. (p2741r3)
static_assert can now be used with a format string. Here’s a nice example from the proposal p2741r3. I made a complete program out of it.
// static_assert26.cpp #include <iostream> #include <format> template <typename T, auto Expected, unsigned long Size = sizeof(T)> constexpr bool ensure_size() { static_assert(sizeof(T) == Expected, "Unexpected sizeof"); return true; } struct S { int _{}; }; int main() { std::cout << std::boolalpha << "C++11\n"; static_assert(ensure_size<S, 1>()); std::cout << std::boolalpha << "C++26\n"; static_assert(sizeof(S) == 1, std::format("Unexpected sizeof: expected 1, got {}", sizeof(S))); std::cout << '\n'; }
The function template ensure_size is defined to take three parameters: a type T, an expected size Expected, and an optional parameter Size which defaults to the size of T. Inside the function, a static_assert statement checks if the size of T is equal to Expected. If the sizes do not match, the compilation will fail with the message “Unexpected sizeof“. The function returns true if the assertion passes.
The program then defines a simple structure S containing a single integer member _. This structure is used to demonstrate the static_assert functionality.
In the main function, the program first prints “C++11” to the console with std::boolalpha to format boolean values as true or false. It then calls static_assert with, which checks if the size of S is 1 byte. Since the size of S is actually larger than 1 byte, this assertion will fail, causing a compilation error.
Next, the program prints “C++26” to the console and uses another static_assert. This time std::format is used. If the size of S is not 1 byte but 4, the compilation will fail.
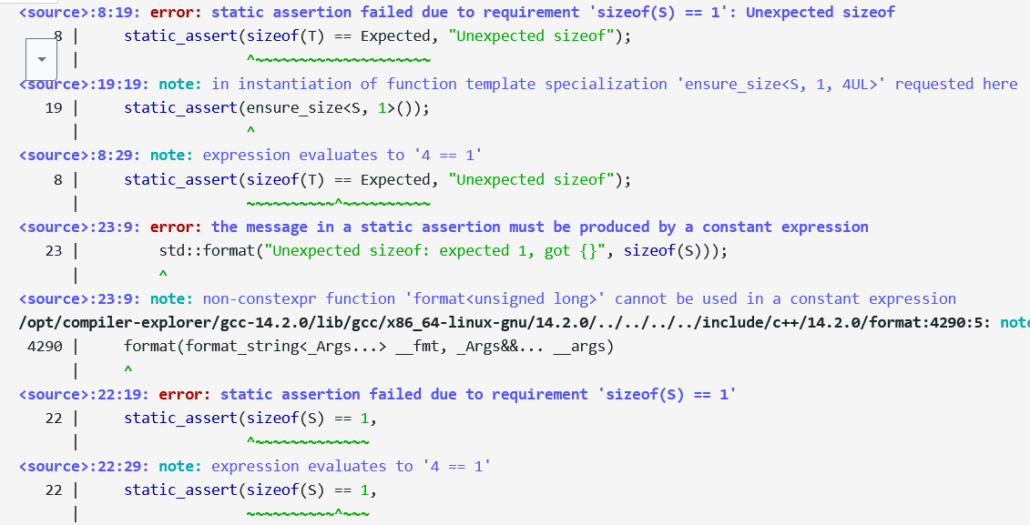
When you study GCC error messages, you will find three errors. std::format is so far not constexpr.
Pack Indexing
Pack indexing may be your favorite template improvement if you are template metaprogramming friend.
The following example is based on the proposal P2662R3.
// packIndexing.cpp #include <iostream> #include <string> template <typename... T> constexpr auto first_plus_last(T... values) -> T...[0] { return T...[0](values...[0] + values...[sizeof...(values)-1]); } int main() { std::cout << '\n'; using namespace std::string_literals; std::string hello = first_plus_last("Hello"s, "world"s, "goodbye"s, "World"s); std::cout << "hello: " << hello << '\n'; constexpr int sum = first_plus_last(1, 2, 10); std::cout << "sum: " << sum << '\n'; std::cout << '\n'; }
The provided example is a function template that computes the sum of a parameter pack’s first and last elements.
The function is defined as a template that takes a variadic number of parameters of any type T. The function’s return type is specified using a trailing return type syntax.
The function body returns the sum of the first and last elements of the parameter pack. The expression values...[0] accesses the first element and values...[sizeof...(values)-1] accesses the last element.
Here’s the output of the program:
 Modernes C++ Mentoring
Modernes C++ Mentoring
Do you want to stay informed: Subscribe.

delete with reason
With C++26, you can specify a reason for your delete. I assume this will become best practice. The following program shall make this clear.
// deleteReason.cpp #include <iostream> void func(double){} template <typename T> void func(T) = delete("Only for double"); int main(){ std::cout << '\n'; func(3.14); func(3.14f); std::cout << '\n'; }
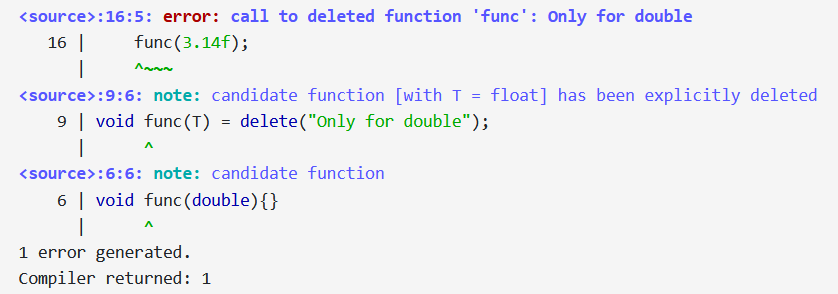
The function func is overloaded in two ways. The first overload is a regular function that takes a double as its parameter. This function can be called with a double argument without any issues.
The second overload is a function template that can take any type as its parameter. However, this function is explicitly deleted using the = delete specifier with a custom message "Only for double". This means that any instantiation of with a type other than double will result in a compilation error, and the provided message will be displayed.
In the main function, the program calls func with the argument 3.14, which is a double. This call is valid and will invoke the non-template overload of func.
Next, the program attempts to call func with the argument 3.14f, which is a float. Since there is no non-template overload of func that takes a float, the template function would be instantiated. However, because the template function is deleted for any type other than double, this call will result in a compilation error with the message "Only for double".
What is Next?
I will directly jump into the C++26 library in my next blog post.
Thanks a lot to my Patreon Supporters: Matt Braun, Roman Postanciuc, Tobias Zindl, G Prvulovic, Reinhold Dröge, Abernitzke, Frank Grimm, Sakib, Broeserl, António Pina, Sergey Agafyin, Андрей Бурмистров, Jake, GS, Lawton Shoemake, Jozo Leko, John Breland, Venkat Nandam, Jose Francisco, Douglas Tinkham, Kuchlong Kuchlong, Robert Blanch, Truels Wissneth, Mario Luoni, Friedrich Huber, lennonli, Pramod Tikare Muralidhara, Peter Ware, Daniel Hufschläger, Alessandro Pezzato, Bob Perry, Satish Vangipuram, Andi Ireland, Richard Ohnemus, Michael Dunsky, Leo Goodstadt, John Wiederhirn, Yacob Cohen-Arazi, Florian Tischler, Robin Furness, Michael Young, Holger Detering, Bernd Mühlhaus, Stephen Kelley, Kyle Dean, Tusar Palauri, Juan Dent, George Liao, Daniel Ceperley, Jon T Hess, Stephen Totten, Wolfgang Fütterer, Matthias Grün, Phillip Diekmann, Ben Atakora, Ann Shatoff, Rob North, Bhavith C Achar, Marco Parri Empoli, Philipp Lenk, Charles-Jianye Chen, Keith Jeffery, Matt Godbolt, Honey Sukesan, bruce_lee_wayne, Silviu Ardelean, schnapper79, Seeker, and Sundareswaran Senthilvel.
Thanks, in particular, to Jon Hess, Lakshman, Christian Wittenhorst, Sherhy Pyton, Dendi Suhubdy, Sudhakar Belagurusamy, Richard Sargeant, Rusty Fleming, John Nebel, Mipko, Alicja Kaminska, Slavko Radman, and David Poole.
| My special thanks to Embarcadero |  |
| My special thanks to PVS-Studio |  |
| My special thanks to Tipi.build |  |
| My special thanks to Take Up Code |  |
| My special thanks to SHAVEDYAKS |  |
Modernes C++ GmbH
Modernes C++ Mentoring (English)
Rainer Grimm
Yalovastraße 20
72108 Rottenburg
Mail: schulung@ModernesCpp.de
Mentoring: www.ModernesCpp.org